摘要
JDK:1.8.0_202
MyBatis Version:3.5.9
# 一:前言
由于Java中的基本类型会有默认值,例如当某个类中存在 private int age; 字段时,创建这个类时,age会有默认值0。在某些情况下,便无法实现使age为null。并且在动态SQL的部分,如果使用 age != null 进行判断,结果总会为true,因而会导致很多隐藏的问题。
所以,在实体类中不要使用基本类型。基本类型包括byte、int、short、long、float、double、char、boolean。
使用下面内容时,需要调节上一章节的日志控制,在 mybatis-config.xml 中,更改 <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
# 二:XML
MyBatis 3.0相比2.0版本的一个最大变化,就是支持使用接口来调用方法。
以前使用SqlSession通过命名空间调用MyBatis方法时,首先需要用到命名空间和方法id 组成的字符串来调用相应的方法。当参数多于 1 个的时候,需要将所有参数放到一个 Map对象中。通过Map传递多个参数,使用起来很不方便,而且还无法避免很多重复的代码。
使用接口调用方式就会方便很多,MyBatis使用Java的动态代理可以直接通过接口来调用相应的方法,不需要提供接口的实现类,更不需要在实现类中使用SqlSession以通过命名空间间接调用。另外,当有多个参数的时候,通过参数注解@Param设置参数的名字省去了手动构造Map参数的过程,尤其在Spring中使用的时候,可以配置为自动扫描所有的接口类,直接将接口注入需要用到的地方。
# 2.1 mapper
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="top.qform.mapper.CustomersMapper">
</mapper>
2
3
4
<mapper>根标签的namespace属性,当Mapper接口和XMLL文件关联的时候,命名空间namespace的值需要配置成接口的全限定名称。MyBatis 内部就是通过这个值将接口和XML关联起来的。如果没有接口,则改成XML自身全路径限定,例如 src/main/resources/mapper/CustomersMapper.xml 则改为 \<mapper namespace="mapper.CustomersMapper">
# 2.2 resultMap
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="top.qform.mapper.CustomersMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="top.qform.model.Customers">
<id column="cust_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="custId"/>
<result column="cust_name" jdbcType="CHAR" property="custName"/>
<result column="cust_address" jdbcType="CHAR" property="custAddress"/>
</resultMap>
</mapper>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
<resultMap> — 用于配置 Java 对象的属性和查询结果列的对应关系。下面是该标签所拥有的属性。
- id:必填,唯一标识,在select标签中,resultMap指定的值即为此处id所设置的值;
- type:必填,用于配置查询列所映射到的Java对象类型;
- extends:选填,可以配置当前的resultMap继承自其他的resultMap,属性值为继承resultMap的id;
- autoMapping:选填,可选值为true或false,用于配置是否启用非映射字段(没有在 resultMap 中配置的字段)的自动映射功能,该配置可以覆盖全局的autoMappingBehavior配置。
下面是 <resultMap> 标签的子标签:
- constructor:配置使用构造方法注入结果,包含以下两个子标签,对应 resultMap 的 id、result 标签,含义相同,注入方式不同;
- idArg:id参数,标记结果作为id(唯一值),可以帮助提高整体性能,对应 resultMap 的 id;
- id:注入到构造方法的一个普通结果,对应 resultMap 的 result。
- id:一个id结果,标记结果作为id(唯一值),可以帮助提高整体性能;
- column:从数据库中得到的列名,或者是列的别名;
- property:映射到列结果的属性。可以映射简单的如 "username" 这样的属性,也可以映射一些复杂对象中的属性,例如 "address.street.number",这会通过 "." 方式的属性嵌套赋值;
- javaType:一个Java类的完全限定名,或一个类型别名(通过typeAlias配置或者默认的类型)。如果映射到一个 JavaBean,MyBatis 通常可以自动判断属性的类型。如果映射到HashMap,则需要明确地指定javaType属性;
- jdbcType:列对应的数据库类型。JDBC 类型仅仅需要对插入、更新、删除操作可能为空的列进行处理。这是JDBC jdbcType的需要,而不是MyBatis的需要;
- typeHandler:使用这个属性可以覆盖默认的类型处理器。这个属性值是类的完全限定名或类型别名。
- result:注入到Java对象属性的普通结果,属性与id属性一样,属性值是通过setter方法注入。两标签不同在于id代表主键;
- association:一个复杂的类型关联,许多结果将包成这种类型;
- collection:复杂类型的集合;
- discriminator:根据结果值来决定使用哪个结果映射;
- case:基于某些值的结果映射。
# 2.3 select
customersMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="top.qform.mapper.CustomersMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="top.qform.model.Customers">
<id column="cust_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="custId"/>
<result column="cust_name" jdbcType="CHAR" property="custName"/>
<result column="cust_address" jdbcType="CHAR" property="custAddress"/>
</resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
cust_id, cust_name, cust_address
</sql>
<select id="selectById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT <include refid="Base_Column_List" /> FROM customers WHERE cust_id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="selectAll" resultType="top.qform.model.Customers">
SELECT cust_id AS custId, cust_name AS custName, cust_address AS custAddress FROM customers
</select>
</mapper>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
CustomersMapper.java
public interface CustomersMapper {
Customers selectById(Integer id);
List<Customers> selectAll();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
Customers.java
public class Customers {
private Integer custId;
private String custName;
private String custAddress;
// getter 和 setter
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
测试类:
public class CustomersTest {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@BeforeClass
public static void init() {
try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml")) {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectAll() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 如果下面语句报错,需要指定全限定 List<Customers> customers = sqlSession.selectList("top.qform.mapper.CustomersMapper.selectAll");
List<Customers> customers = sqlSession.selectList("selectAll");
customers.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
接口和XML是通过将namespace的值为接口的全限定名称来进行关联
虽然方法有重载,但是XML中的值不能重复,因此XML对应的接口里面的方法重载会报错。
<select> — 映射查询语句使用的标签,下面是该标签所拥有的属性。
- id:命名空间中的唯一标识符,用来代表这条语句的标识;
- resultMap:用于设置返回值的类型和映射关系。
- resultMap:用于设置返回值的类型
名称映射规则
仔细观察上面的 selectById 和 selectAll,其中 selectById 使用了 resultMap 来设置结果映射,而 selectAll 中则通过 resultType 直接指定了返回结果类型,但需要在 DML 中为所有列名和属性不一致的列设置别名,使得最终的查询结果列和resultType指定的对象属性名保持一致,进而实现自动映射。
如果不用别名,仅仅是大小驼峰的区别,可以修改MyBatis配置,开启自动驼峰命名规则,如,在自定义的 mybatis-config.xml 配置可以如下配置:
<configuration> <settings> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> </settings> </configuration>1
2
3
4
5在实际匹配的时候,MyBatis会先将两者都转换为大写形式,然后判断是否相同,即 property="userName" 和 property="userName" 都可以匹配到对象的userName属性上。判断是否相同的时候要使用USERNAME,因此在设置property属性或别名的时候,不需要考虑大小写是否一致,但是为了便于阅读,要尽可能按照统一的规则来设置。
含拓展字段:
在联表查询时候,可能需要其他表的一些字段结果返回。这时候 POJO 有几种处理方式。以上面 Customers 为例。
方法一:直接在 Customers 添加字段 userName 方法二:继承实现
public class CustomersExtend extends Customers {
private String userName;
// getter 和 setter
}
2
3
4
5
6
方法三:上面两种方法适合少量字段,拓展字段多,可以考虑组合
public class Customers {
// 其他原有字段
// 用户信息表(userName 来源)
private User user;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
xml中使用别名时,需要指定为 "字段名.属性名",例如下面 "user.userName",通过这种方式,将值赋予user字段中的userName属性。
<select id="selectAll" resultType="top.qform.model.Customers">
SELECT
c.cust_id AS custId, c.cust_name AS custName, c.cust_address AS custAddress,
u.user_name AS user.userName
FROM customers c LEFT JOIN user u ON c.cust_id = u.cust_id
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
# 2.4 insert
CustomersMapper.xml
<insert id="insert" parameterType="top.qform.model.Customers">
insert into customers (cust_name, cust_address)
values (#{custName}, #{custAddress,jdbcType=CHAR})
</insert>
2
3
4
CustomersMapper.java
public interface CustomersMapper {
int insert(Customers customers);
}
2
3
4
5
测试类:
@Test
public void testInsert() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CustomersMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CustomersMapper.class);
Customers customers = new Customers();
customers.setCustAddress("gd gz");
customers.setCustName("gd");
// 返回值 result 是执行的 SQL 影响的行数
int result = mapper.insert(customers);
// 只插入1条数据
Assert.assertEquals(1, result);
} finally {
// 为了不影响其他测试,这里选择回滚
// 由于默认的 sqlSessionFactory.openSession() 是不会自动提交的
// 因此不手动执行 commit 也不会提交到数据库
assert sqlSession != null;
sqlSession.rollback();
// 关闭sqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
为了防止类型错误,对于一些特殊的数据类型,建议指定具体的 jdbcType 值。例如 BLOB类型,TIMESTAMP类型等。BLOB对应的类型是ByteArrayInputStream,就是二进制数据流。 由于数据库区分date、time、datetime类型,但是Java中一般都使用java.util.Date类型。因此为了保证数据类型的正确,需要手动指定日期类型,date、time、datetime对应的JDBC类型分别为DATE、TIME、TIMESTAMP。
<insert> — 映射插入语句使用的标签,下面是该标签所拥有的属性。
- id:命名空间中的唯一标识符,可用来代表这条语句。
- parameterType:即将传入的语句参数的完全限定类名或别名。这个属性是可选的,因为MyBatis可以推断出传入语句的具体参数,因此不建议配置该属性。
- flushCache:默认值为true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会清空一级缓存和二级缓存。
- timeout:设置在抛出异常之前,驱动程序等待数据库返回请求结果的秒数。
- statementType:对于STATEMENT、PREPARED、CALLABLE,MyBatis会分别使用对应的 Statement、PreparedStatement、CallableStatement,默认值为PREPARED。
- useGeneratedKey:默认值为 false。如果设置为 true,MyBatis 会使用 JDBC的getGeneratedKeys方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键。
- keyProperty:MyBatis通过getGeneratedKeys获取主键值后将要赋值的属性名。如果希望得到多个数据库自动生成的列,属性值也可以是以逗号分隔的属性名称列表。
- keyColumn:仅对INSERT和UPDATE有用。通过生成的键值设置表中的列名,这个设置仅在某些数据库(如 PostgreSQL)中是必须的,当主键列不是表中的第一列时需要设置。如果希望得到多个生成的列,也可以是逗号分隔的属性名称列表。
- databaseId:如果配置了databaseIdProvider,MyBatis会加载所有的不带databaseId的或匹配当前databaseId的语句。如果同时存在带databaseId和不带databaseId的语句,后者会被忽略。
获取组件自增的值
<insert id="insert2" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="custId">
insert into customers (cust_name, cust_address)
values (#{custName}, #{custAddress,jdbcType=CHAR})
</insert>
2
3
4
useGeneratedKeys 设置为true后,MyBatis会使用JDBC的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键。获得主键值后将其赋值给 keyProperty 配置的 custId 属性。当需要设置多个属性时,使用逗号隔开,这种情况下通常还需要设置 keyColumn 属性,按顺序指定数据库的列,这里列的值会和keyProperty配置的属性一一对应。
单元测试
// 返回值 result 是执行的 SQL 影响的行数
int result = mapper.insert2(customers);
// 只插入1条数据
Assert.assertEquals(1, result);
System.out.println(customers.getCustId());
2
3
4
5
# 2.5 selectKey
上面这种回写主键的方法只适用于支持主键自增的数据库。有些数据库(如 Oracle)不提供主键自增的功能,而是使用序列得到一个值,然后将这个值赋给id,再将数据插入数据库。对于这种情况,可以采用另外一种方式:使用 <selectKey> 标签来获取主键的值,这种方式不仅适用于不提供主键自增功能的数据库,也适用于提供主键自增功能的数据库。
MySQL
<insert id="insert3">
insert into customers (cust_name, cust_address)
values (#{custName}, #{custAddress,jdbcType=CHAR})
<selectKey keyColumn="cust_id" resultType="int" keyProperty="custId" order="AFTER">
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
</insert>
2
3
4
5
6
7
Oracle
<insert id="insert3">
<selectKey keyColumn="cust_id" resultType="int" keyProperty="custId" order="BEFORE">
SELECT SEQ_ID.nextval from dual
</selectKey>
insert into customers (cust_name, cust_address)
values (#{custName}, #{custAddress,jdbcType=CHAR})
</insert>
2
3
4
5
6
7
selectKey元素的位置放在insert之前或之后,不会影响selectKey中的方法在insert前面或者后面执行的顺序,影响执行顺序的是 order 属性。
Oracle方式的INSERT语句中明确写出了id列和值#{id},因为执行selectKey中的语句后 custId 就有值了,需要把这个序列值作为主键值插入到数据库中,所以必须指定 custId 列,如果不指定这一列,数据库就会因为主键不能为空而抛出异常。
以下是其他一些支持主键自增的数据库配置 selectKey 中回写主键的 SQL。
- DB2:
VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL() - MYSQL:
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() - SQLSERVER:
SELECT SCOPE_IDENTITY() - CLOUDSCAPE:
VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL() - DERBY:
VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL() - HSQLDB:
CALL IDENTITY() - SYBASE:
SELECT@@IDENTITY() - DB2_MF:
SELECT IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL() FROM SYSIBM.SYSDUMMY1 - INFORMIX:
select dbinfo('sqlca.sqlerrd1') from systables where tabid=1
# 2.6 update
CustomersMapper.xml
<update id="updateById">
UPDATE customers
SET cust_name = #{custName}, cust_address = #{custAddress}
WHERE cust_id = #{custId}
</update>
2
3
4
5
CustomersMapper.java
public interface CustomersMapper {
int updateById(Customers customers);
}
2
3
4
5
# 2.7 delete
CustomersMapper.xml
<delete id="deleteById" >
DELETE FROM customers
WHERE cust_id = #{custId}
</delete>
2
3
4
CustomersMapper.java
public interface CustomersMapper {
int deleteById(Integer custId);
}
2
3
4
5
# 三:入参
当 Mapper.xml 中有多个参数时,对应的 Mapper 接口有几种入参写法。
- 单个入参,例如上面的 deleteById 方法,可以普通入参,直接使用;
- 多个入参
- JavaBean,例如上面的 insert、update 方法;
- Map,通过Map的key-value方式传递参数值,key来映射XML中SQL使用的参数值名字,value用来存放参数值,由于这种方式还需要手动创建Map以及对参数进行赋值,其实并不简洁,故而不推荐;
- @Param
# 3.1 异常
如果多个参数,但是不用上面说的几种方式,就当作普通入参会如何?
修改上面的insert方法
CustomersMapper.xml
<insert id="insert">
insert into customers (cust_name, cust_address)
values (#{custName}, #{custAddress})
</insert>
2
3
4
CustomersMapper.java
public interface CustomersMapper {
int insert(String custName, String custAddress);
}
2
3
运行结果
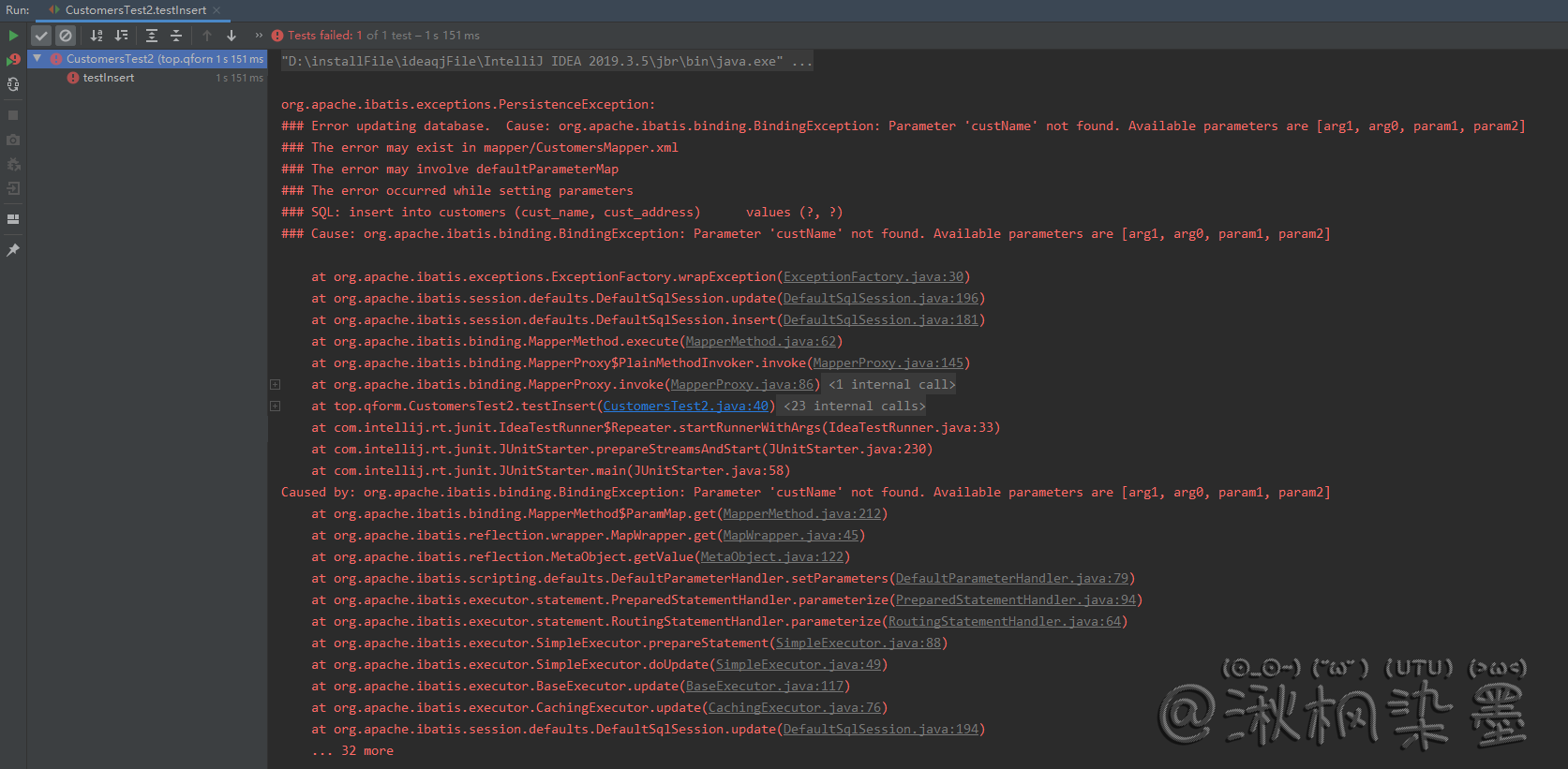
可以发现 PersistenceException 和 BindingException,根据 BindingException 错误提示,XML可用的参数只有 [arg1, arg0, param1, param2],这时候如果XML中的 #{custName} 换成 #{arg0} 或 param1 和 #{custAddress} 换成 #{arg1} 或 param2 就会发现正常调用,不过不建议这么使用。
# 3.2 @Param
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
public interface CustomersMapper {
int insert(@Param("custName") String custName, @Param("custAddress") String custAddress);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
给参数配置@Param注解后,MyBatis就会自动将参数封装成Map类型,@Param注解值会作为Map中的key,因此在SQL部分就可以通过配置的注解值来使用参数。
当只有一个参数(基本类型或拥有TypeHandler配置的类型)的时候,MyBatis不关心这个参数叫什么名字就会直接把这个唯一的参数值拿来使用。
# 3.3 多个JavaBean
如果入参有多个JavaBean,这时候主要XML会变化的比较大,例如:
CustomersMapper.java
List<Customers> selectCondition(@Param("customer") Customers customer, @Param("user") User user)
CustomersMapper.xml
<select id="selectAll" resultType="top.qform.model.Customers">
SELECT
c.cust_id AS custId, c.cust_name AS custName, c.cust_address AS custAddress,
u.user_name AS user.userName
FROM customers c LEFT JOIN user u ON c.cust_id = u.cust_id
WHERE user_name = #{user.userName} AND cust_name = #{customer.custName}
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 四:注解
MyBatis注解方式就是将SQL语句直接写在接口上。这种方式的优点是,对于需求比较简单的系统,效率较高。缺点是,当SQL有变化时都需要重新编译代码,一般情况下不建议使用注解方式。
# 4.1 @Select
public interface Customers2Mapper {
@Select("SELECT cust_id, cust_name, cust_address FROM customers WHERE cust_id = #{id}")
Customers selectById1(Integer id);
}
2
3
4
5
6
映射转换:
- SQL使用别名
- 配置加入mapUnderscoreToCamelCase,自动转换大小驼峰
- @Results
# 4.2 @Results
@Results({
@Result(property = "custId", column = "cust_id", id = true),
@Result(property = "custName", column = "cust_name"),
@Result(property = "custAddress", column = "cust_address")
})
@Select("SELECT cust_id, cust_name, cust_address FROM customers WHERE cust_id = #{id}")
Customers selectById2(Integer id);
2
3
4
5
6
7
- @Results 对应XML中的 <resultMap> 元素
- @Result 对应XML中的 <result> 元素
- id=true 对应 <id> 元素
MyBatis 3.3.1 之后,@Results 注解增加了一个id属性,设置了id属性后,就可以通过id属性引用同一个 @Results 配置了
Results(id = "customerBase", value = {
@Result(property = "custId", column = "cust_id", id = true),
@Result(property = "custName", column = "cust_name"),
@Result(property = "custAddress", column = "cust_address")
})
@Select("SELECT cust_id, cust_name, cust_address FROM customers WHERE cust_id = #{id}")
Customers selectById2(Integer id);
@ResultMap("customerBase")
@Select("SELECT cust_id, cust_name, cust_address FROM customers")
Customers selectAll();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
测试:
public class CustomersTest3 {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@BeforeClass
public static void init() {
try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml")) {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectById2() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
Customers2Mapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(Customers2Mapper.class);
// 调用 selectById2 方法,查询 id = 10001 的信息
Customers customers = mapper.selectById2(10001);
Assert.assertNotNull(customers);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
如果直接运行,就会发现报如下错误,所以还需要指定mapper
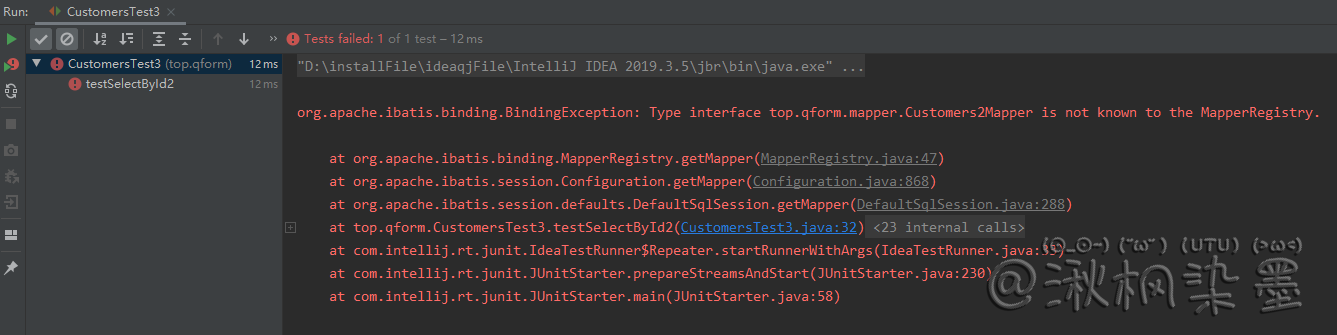
mybatis-config.xml
<mappers>
<mapper class="top.qform.mapper.Customers2Mapper"/>
</mappers>
2
3
# 4.3 @Insert
普通用法
@Insert("insert into customers (cust_name, cust_address) values (#{custName}, #{custAddress,jdbcType=CHAR})")
int insert1(Customers customers);
2
返回自增主键
@Insert("insert into customers (cust_name, cust_address) values (#{custName}, #{custAddress,jdbcType=CHAR})")
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "custId")
int insert2(Customers customers);
2
3
返回非自增主键
@Insert("insert into customers (cust_name, cust_address) values (#{custName}, #{custAddress,jdbcType=CHAR})")
@SelectKey(statement = "SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()", keyProperty = "custId", resultType = Integer.class, before = false)
int insert3(Customers customers);
2
3
before 为 false 时功能等同于 order="AFTER",before为true时功能等同于 order="BEFORE"
测试:
@Test
public void testInsert() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Customers2Mapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(Customers2Mapper.class);
Customers customers = new Customers();
customers.setCustId(33);
customers.setCustAddress("gd gz");
customers.setCustName("gd");
int result = mapper.insert2(customers);
System.out.println(customers.getCustId());
result = mapper.insert3(customers);
System.out.println(customers.getCustId());
} finally {
// 为了不影响其他测试,这里选择回滚
// 由于默认的 sqlSessionFactory.openSession() 是不会自动提交的
// 因此不手动执行 commit 也不会提交到数据库
assert sqlSession != null;
sqlSession.rollback();
// 关闭sqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 4.4 @Update
@Update("UPDATE customers SET cust_name = #{custName}, cust_address = #{custAddress} WHERE cust_id = #{custId}")
int updateById(Customers customers);
2
# 4.5 @Delete
@Delete("insert into customers (cust_name, cust_address) values (#{custName}, #{custAddress})")
int deleteById(Integer custId);
2
# 4.6 Provider
- @SelectProvider
- @InsertProvider
- @UpdateProvider
- @DeleteProvider
CustomersProvider.java
public class CustomersProvider {
public String selectById(final Integer id) {
return new SQL() {
{
SELECT("cust_id, cust_name, cust_address");
FROM("customers");
WHERE("cust_id = #{id}");
}
}.toString();
}
public String selectAll() {
return "SELECT cust_id, cust_name, cust_address FROM customers";
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Customers3Mapper.java
public interface Customers3Mapper {
@SelectProvider(type = CustomersProvider.class, method = "selectById")
Customers selectById(Integer id);
@SelectProvider(type = CustomersProvider.class, method = "selectAll")
Customers selectAll();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
mybatis-config.xml
<mappers>
<mapper class="top.qform.mapper.Customers3Mapper"/>
</mappers>
2
3
测试
public class CustomersTest4 {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@BeforeClass
public static void init() {
try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml")) {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectAll() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
Customers3Mapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(Customers3Mapper.class);
// 调用 selectById2 方法,查询 id = 10001 的信息
Customers customers = mapper.selectById(10001);
Assert.assertNotNull(customers);
// 返回全部
System.out.println(mapper.selectAll().size());
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 五:动态SQL
MyBatis3 之后的版本采用了功能强大的 OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language)表达式语言,以下是MyBatis的动态SQL在XML中支持的几种标签。
- if
- choose(when、oterwise)
- trim(where、set)
- foreach
- bind
# 5.1 if
通常用于 WHERE 语句中,通过判断参数值来决定是否使用某个查询条件,也经常用于 UPDATE 语句中判断是否更新某一个字段,和在 INSERT 语句中用来判断是否插入某个字段的值。
CustomersMapper.xml
<select id="selectCondition" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT <include refid="Base_Column_List" />
FROM customers
WHERE 1 = 1
<if test="null != custName and '' != custName">
and cust_name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{custName} ,'%')
</if>
<if test="null != custAddress and '' != custAddress">
and cust_address LIKE CONCAT('%', #{custAddress} ,'%')
</if>
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
CustomersMapper.java
public interface CustomersMapper {
List<Customers> selectCondition(Customers customers);
}
2
3
测试:
@Test
public void testSelectCondition() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
CustomersMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CustomersMapper.class);
Customers customers = new Customers();
customers.setCustAddress("gd");
customers.setCustName("gd");
System.out.println(mapper.selectCondition(customers));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
- test属性必填,表达式结果可以是true或false,除此之外所有的非0值都为true,只有0为false。
- 判断条件
property != null或property == null,适用于任何类型的字段,用于判断属性值是否为空。 - 判断条件
property != ''或property == '',仅适用于String类型的字段,用于判断是否为空字符串。 - and和or:当有多个判断条件时,使用and或or进行连接,嵌套的判断可以使用小括号分组,and相当于Java中的与(&&),or相当于Java中的或(||)
# 5.2 choose
choose 元素中包含 when 和 otherwise 两个标签,至少有一个 when。效果 if...else...
<select id="selectCondition" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT <include refid="Base_Column_List" />
FROM customers
WHERE 1 = 1
<choose>
<when test="null != custId">
and cust_id = #{custId}
</when>
<when test="null != custName and '' != custName">
and cust_name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{custName} ,'%')
</when>
<otherwise>
and 1 = 2
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
上面的SQL,当参数 custId 有值的时候优先使用 custId 查询;当 custId 无值时就去判断 custName 是否有值,如果有值就用 custName;如果再无值, 则走 otherwise 恒为false,查询不到结果。
# 5.3 where
where和set都属于trim的一种具体用法
where 标签作用,如果该标签包含的元素中有返回值,就插入一个where;如果where后面的字符串是以 AND 和 OR 开头的,就将它们剔除。
<select id="selectCondition" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT <include refid="Base_Column_List"/>
FROM customers
<where>
<if test="null != custName and '' != custName">
and cust_name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{custName} ,'%')
</if>
<if test="null != custAddress and '' != custAddress">
and cust_address LIKE CONCAT('%', #{custAddress} ,'%')
</if>
</where>
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 5.4 set
set标签作用,如果该标签包含的元素中有返回值,就插入一个set;如果set后面的字符串是以逗号结尾的,就将这个逗号剔除。
<update id="updateById">
UPDATE customers
<set>
<if test="null != custId and '' != custId">
cust_id = #{custId},
</if>
<if test="null != custName and '' != custName">
cust_name = #{custName},
</if>
<if test="null != custAddress and '' != custAddress">
cust_address = #{custAddress}
</if>
</set>
WHERE custId = #{custId}
</update>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
全部的查询条件都是null或者空,如果有 custId = #{custId} 这个条件,最终的SQL,UPDATE customers SET cust_id = #{custId} WHERE custId = #{custId},所以为了避免错误产生, custId = #{custId} 仍有保留的必要。
# 5.5 trim
where 和 set 标签的功能都可以用 trim 标签来实现,并且在底层就是通过 TrimSqlNode 实现的。
where 标签对应 trim 的实现如下:
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR ">
...
</trim>
2
3
AND 和 OR 后面的空格不能省略,为了避免匹配到 andes、orders 等词。
实际的 prefixOverrides 包含 "AND"、"OR"、"AND\n"、"OR\n"、"AND\r"、"OR\r"、"AND\t"、"OR\t"
set 标签对应 trim 的实现如下:
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
...
</trim>
2
3
trim 标签属性:
- prefix:给内容增加prefix指定的前缀;
- prefixOverrides:把内容中匹配的前缀字符串去掉;
- suffix:给内容增加suffix指定的后缀;
- suffixOverrides:把内容中匹配的后缀字符串去掉。
# 5.6 foreach
SQL 语句中使用 IN 关键字,如 id in (1,2,3)。可使用 ${ids} 方式直接取值,但这种写法不能防止SQL注入,想避免SQL注入就需要用 #{},这时就需要配合使用 foreach 标签。
foreach 可处理数组、Map、实现Iterable接口的对象。数组在处理时会转换为List对象,所以foreach 遍历对象分两大类,Iterator类型和Map类型
<select id="selectByIds" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT <include refid="Base_Column_List"/>
FROM customers
WHERE cust_id IN
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="custId" index="i">
#{custId}
</foreach>
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
CustomersMapper.java
List<Customers> selectByIds(List<Integer> ids);
测试
@Test
public void testSelectByIds() {
List<Integer> list = IntStream.range(10001, 10010).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
CustomersMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CustomersMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectByIds(list).size());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
foreach 包含以下属性:
- collection:必填,值为要迭代循环的属性名。这个属性值的情况有很多;
- item:变量名,值为从迭代对象中取出的每一个值;
- index:索引的属性名,在集合数组情况下值为当前索引值,当迭代循环的对象是Map类型时,这个值为Map的key(键值);
- open:整个循环内容开头的字符串;
- close:整个循环内容结尾的字符串;
- separator:每次循环的分隔符。
DefaultSqlSession源码
package org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults;
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement) {
return this.selectList(statement, null);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
return selectList(statement, parameter, rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
}
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
private Object wrapCollection(final Object object) {
return ParamNameResolver.wrapToMapIfCollection(object, null);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
ParamNameResolver源码
package org.apache.ibatis.reflection;
public class ParamNameResolver {
/**
* 如果对象是 Collection 或 数组,则包装到 ParamMap
*
* @param object parameter 对象
* @param actualParamName 实际参数名称(如果指定名称,则将对象设置为具有指定名称的 ParamMap)
* @return ParamMap 对象
* @since 3.5.5
*/
public static Object wrapToMapIfCollection(Object object, String actualParamName) {
if (object instanceof Collection) {
ParamMap<Object> map = new ParamMap<>();
map.put("collection", object);
if (object instanceof List) {
map.put("list", object);
}
Optional.ofNullable(actualParamName).ifPresent(name -> map.put(name, object));
return map;
} else if (object != null && object.getClass().isArray()) {
ParamMap<Object> map = new ParamMap<>();
map.put("array", object);
Optional.ofNullable(actualParamName).ifPresent(name -> map.put(name, object));
return map;
}
return object;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
- 当类型为集合时,会转换 ParamMap 类型,并添加一个 key 为 collection 的值;
- 当类型为 List 时,除了添加 collection 这个key,还会添加一个 key 为 list,所以 XML 中
collection="list"时,就能得到这个集合,并对他进行循环操作; - 当类型为数组时,也会转换 ParamMap,默认添加一个 array 的 key,所以 XML 中可以写为
collection="array" - actualParamName 这个值,是由Mapper中手动使用
@Param指定的名称,所以一旦使用注解,XML中就可以使用一样的名称与之对应。
批量插入
<insert id="insertList">
INSERT INTO customers (cust_name, cust_address)
VALUES
<foreach collection="list" item="ct" separator=",">
(#{ct.custName}, #{ct.custAddress})
</foreach>
</insert>
2
3
4
5
6
7
通过 item 指定了循环变量名后,在引用值的时候使用的是 "属性.属性" 的方式,如 ct.custName
int insertList(List<Customers> customersList);
测试
@Test
public void testInsertList() {
List<Customers> list = IntStream.range(10300, 10305).mapToObj(Customers::new).collect(Collectors.toList());
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CustomersMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CustomersMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.insertList(list));
} finally {
assert sqlSession != null;
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
返回自增主键值
- MyBatis 3.3.1 版本(含)开始,支持批量新增回写主键值的功能;
- 仅支持Mysql
<insert id="insertList" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="custId">
... ...
</insert>
2
3
和单次插入一样,使用 useGeneratedKeys 和 keyProperty 两个属性。
动态UPDATE
当参数是Map类型的时候,foreach标签的index属性值对应的不是索引值,而是Map中的key,利用这个key可以实现动态UPDATE。
<update id="updateByMap">
UPDATE customers
SET
<foreach collection="_parameter" item="val" index="key" separator=",">
${key} = #{val}
</foreach>
WHERE cust_id = #{cust_id}
</update>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
int updateByMap(Map<String, Object> map);
测试
@Test
public void testUpdateByMap() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CustomersMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CustomersMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("cust_id", 10043);
map.put("cust_name", "gd gz");
map.put("cust_address", "hz");
// 返回值 result 是执行的 SQL 影响的行数
int result = mapper.updateByMap(map);
// 只更新1条数据
Assert.assertEquals(1, result);
} finally {
assert sqlSession != null;
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 5.7 bind
bind 标签可以使用 OGNL 表达式创建一个变量并将其绑定到上下文中。例如,使用 LIKE 时,经常这样写 cust_name LIKE Concat('%', #{custName}, '%'),使用 concat 函数连接字符串,在MySQL中,这个函数支持多个参数,但在Oracle中只支持两个参数。由于不同数据库之间的语法差异,如果更换数据库,有些SQL语句可能就需要重写。针对这种情况,可以使用 bind 标签来避免由于更换数据库带来的一些麻烦。如下
<if test="null != custName and '' != custName">
<bind name="custNameLike" value="'%' + custName + '%'"/>
AND cust_name LIKE #{custNameLike}
</if>
2
3
4
- name:必填,绑定到上下文的变量名;
- value:必填,OGNL表达式。
# 六:参考文献
- 《MyBatis从入门到精通 - 刘增辉》
- MyBatis官网 (opens new window)
